AV Connections
Which connections give the clearest image?
Connections greatly affect your image quality. Old analog cables are no longer capable of carrying the data 4K UHD images require.
For Home and portable presentations HDMI 1.4 up is recommended. For professional installs HDMI 2.0, SDI and HTBaseT should be considered.
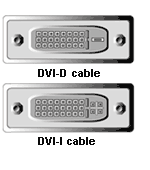
DVI
Digital Video Interface (DVI) cables look a little like a standard VGA cable, but they are slightly larger. Under ideal circumstances, the DVI
cable creates a ‘digital to digital’ connection between video or data source and display device.
The High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) standard has expanded the use of DVI in high definition DVD players and HDTV set top boxes.
Current Types
DVI-A- analog only
DVI-D- digital only, single link or dual link
DVI-I- integrated, combines digital and analog in the same connector; digital may be single or dual link
For a Recommendation:
Call 1300 88 11 79
For a Recommendation:
Call 1300 88 11 79

HDBaseT Cables
The HDBaseT cable combines audio and video signals, USB, network and even power into one single cable and is set to replace HDMI
when it starts hitting shop shelves in 2012.
The cable was designed by the HDBaseT alliance which represents a culmination of efforts from Sony, Samsung, LG and Valens. By combining
all of the normal connections found in the home the companies hope to make the new industry standard. Most current generation displays will
probably be incompatible due to their lack of an ethernet port which supports the cable. The HDBaseT alliance insists that new cables won't
need to be purchased due to the technology working with current network wiring, ethernet cables and an RJ-45 connector.
The cable allows "a network of sources - such as digital video recorders (DVR), Blu-ray disc players, game consoles, PCs and mobile
devices - to be connected directly to displays in multiple locations".
Current HDMI 1.4 cables allow stereoscopic 3D signals to be sent to a TV as well as normal and high definition content. The HDBaseT is capable of
doing the same but also adds the ability to use a 100Mb/sec ethernet connection and up to 100W of charging power.
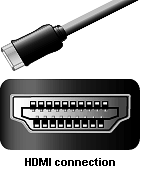
HDMI Cables
High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) cables are a smaller version of DVI cables. With one added feature
HDMI cables can also carry 16 bit, 8 channel, digital audio signals as well as video. HDMI is the best
choice for AV applications.
Developed by Sony, Hitachi, Thomson (RCA), Philips, Matsushita (Panasonic), Toshiba and Silicon Image, the
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) has emerged as the connection standard for HDTV and the consumer
electronics market.
HDMI is the first and only digital interface to combine uncompressed high-definition video, multi-channel
audio and intelligent format and command data in a single digital interface.
HDMI offers significant advantages over analog A/V connections, including the ability to transmit uncompressed
digital video and audio content. In addition to numerous device and display manufacturers, Hollywood studios and cable
and satellite operators also support HDMI.
The Evolution of HDMI
HDMI 1.1 - 2004. Added support for DVD Audio.
HDMI 1.2 - 2005. Added support for One Bit Audio, used on Super Audio
CDs, up to 8 channels.
HDMI 1.2a - 2005. Fully specifies Consumer Electronic Control (CEC)
features, command sets, and CEC compliance tests.
HDMI 1.3 - 2006. Increases single-link bandwidth to 340 MHz (10.2
Gbit/s). Incorporates automatic audio syncing (lip sync) capability. Supports output of Dolby TrueHD and DTS-HD Master
Audio streams for external decoding by AV receivers. TrueHD and DTS-HD are lossless audio codec formats
used on HD DVDs and Blu-ray Discs. If the disc player can decode these streams into uncompressed audio, then HDMI 1.3
is not necessary, as all versions of HDMI can transport uncompressed audio.
HDMI 1.4 - 2009 adds 4K Resolution Support(@ 30hz), 1.07 Billion colours, a data channel to the HDMI connection, enabling high-speed,
bi-directional communication. 3D support.
HDMI 2 - 2013. 4K video (@ 60hz) increases the maximum bandwidth to 18.0 Gbit/s, HDR and rec.2020 colour support
HDMI 2.1 - 2017. 8K video supported, up to 10K (@ 120hz), Dolby Atmos, DPS:X

RJ45 (LAN, Ethernet) Cables
Commonly used to connect technology together over a network, RJ45 cables are mostly used for control purposes with projectors.
There are a limited number of projectors that offer "video over LAN".

Serial Digital Interface (SDI)
SDI is a professional video interface used for broadcast quality video. High Definition Serial Digital Interface (HD-SDI) uses two BNC
connectors and is commonly referred to as Dual Link HD-SDI. SDI uses BNC connectors.
The 5 different standards for SDI are:
Transfer Rates:
SD-SDI - upto 270 Mbit/s
Dual Link SD-SDI - 540 Mbit/s
HD-SDI - 1.485 Gbit/s
Dual Link HD-SDI - 2.970 Gbit/s
3G-SDI - 2.970 Gbit/s


|
USB Cables
Universal Serial Bus (USB) is a serial bus standard to interface devices to a computer. USB was designed to allow
many peripherals to be connected using a single standardized interface socket and to improve the plug-and-play capabilities
by allowing devices to be connected and disconnected without rebooting the computer (hot swapping). Other convenient features
include providing power to low-consumption devices without the need for an external power supply.
USB was originally designed for personal computers, but it has become commonplace on other devices such as PDAs and video
game consoles. As of 2008, there are about 2 billion USB devices in the world. With the advent of Flash Memory Sticks USB
Type A is a convenient way to make presentations with your projector without using a PC.
USB Type B is used a a mouse connection on older projectors and is not compatible
with Flash Memory Sticks. There are also mini versions of USB A & B
commonly found on cameras and mobile phones.
Old Analog and Digital Connections

RCA or Composite Cables
These are the most common cables, used to hook up your standard VCR and
stereo equipment. They are color-coded: red, white, and yellow. Red is
for right audiochannel . White is for left audio channel . Yellow is for
video. The entire video signal is transmitted by one cable. the lowest
quality cable for a video signal. Most televisions, video camcorders,
VCRs, and videodisc players will have RCA jacks for these cables.

BNC Cables
A BNC cable is actually just another form of an RCA/composite cable. The end of the cable looks different from an RCA
cable, but can be changed to an RCA end with an adapter. Most professional video equipment will have a BNC jack instead
of a RCA jack. The physical connection is more secure because BNC cables twist and lock in place.
A BNC Connector is used in Serial Video Interface (SDI) connections. SDI is a professional video interface used for broadcast
quality video. High Definition Serial Digital Interface (HD-SDI) uses two BNC connectors and is commonly referd to as Dual Link HD-SDI.

S-Video or Y/C Cables
Or SVHS cable can be found on most high-end televisions, all videodisc players, camcorders,
digital cable and satellite set top boxes, and SVHS VCRs. S-video cables differ from composite
cables in that they split video signal into two different components: luminance and chrominance.
The S-video cable will offer marked improvement over a composite cable.

Component Cables
Component cables look just like composite cables. The difference is
that, where a composite cable carries the entire video signal on a
single cable, component cables split the signal in three. This
connection gives a superior image over composite or S-video connections.
The signal itself is referred to as either Y,Cr,Cb, or Y,Pb,Pr. The tips
of the cables and jacks will be red, green and blue. Unfortunately, this
can be a bit confusing because computer RGB connections are colored the
same way. A good rule of thumb is that, if the connections are RCA type,
it is usually a component cable. Computer RGB cables will usually be BNC
type. Most high-end DVD players and HDTV tuners will have component
connections.

M1 Cables
The M1 Display Interface System is a standard created by the Video Electronics Standards
Association (VESA).
A consortium of video adapter and monitor manufacturers founded in 1989, whose goal is to standardize video
protocols specifically for digital displays. The M1 standard was approved in
August of 2001.
Compatible with DVI, VGA, USB and Fire Wire signals. The M1-DA connector
replaces the VGA, DVI and USB connectors found on other projectors.
Adaptors are required to connect to a VGA or DVI source. Like USB, M1-DA
can provide power to external devices. The popularity of the M1
connectors is in decline because nearly all connections you will make
will need an adaptor.
Variants of M1 connectors are in line with the DVI types.
M1-DA - Digital and Analog. The most common type. It supports VGA, USB, and DVI signals.
M1-D - Digital. Supports DVI signals
M1-A - Analog. Supports VGA signals.

RGB Cables
These cables look split the video signal into five. There are three different types of RGB cables:
- RGBHV is a five-cable system that splits the video signal for color into red, green, and blue, and then has two more cables to
carry the sync for the signal (horizontal and vertical sync).
- RGB H/V is a four-cable system that splits the color the same way, but has the horizontal and vertical sync on a single fourth cable.
- RGB video cables again split the color signal in three, but carry the additional sync signal on one of the color cables, usually
the green (called RGB sync on green).
An RGBHV signal is the way a computer connects to a projector. Five pins on a 15-pin VGA cable are RGBHV. The projector recognizes the type
of signal and projects accordingly.
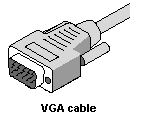
VGA Cables
This is your standard computer monitor cable. It is typically male-to-male with three rows, 15
pins. or computer to projector connections. Some HDTV boxes have connections for VGA.